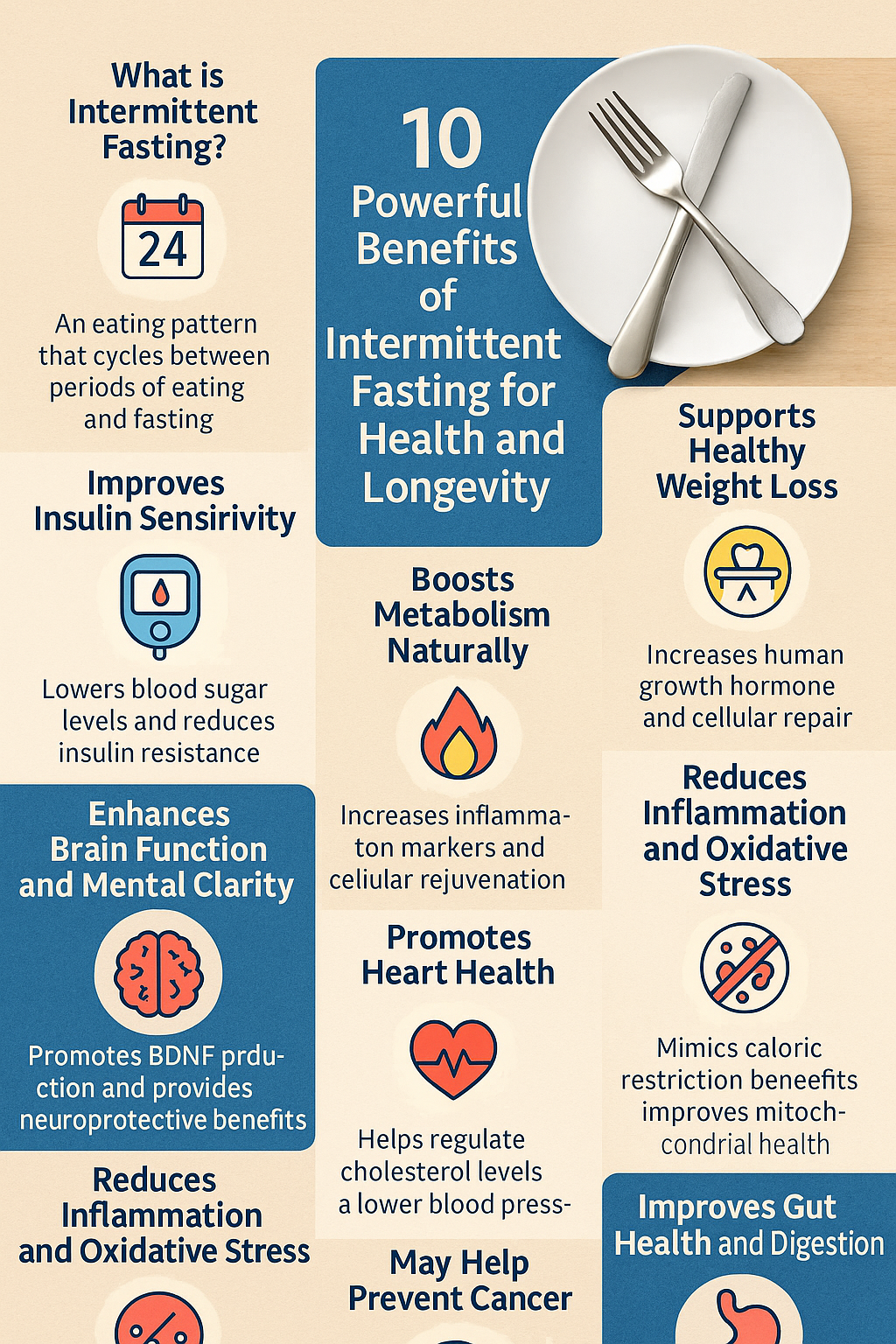
Intermittent fasting (IF) has become one of the most popular health and fitness trends globally—and for good reason. Backed by science and centuries-old practices, intermittent fasting offers a wide range of physical and mental health benefits. From weight loss and improved metabolism to better brain health and longevity, the benefits are impressive. Let’s explore exactly why intermittent fasting might be the lifestyle upgrade you’ve been looking for.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Definition and Concept
Intermittent fasting is not a diet in the traditional sense. Instead, it’s an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. It doesn’t prescribe what foods you should eat but rather when you should eat them.
Types of Intermittent Fasting
- 16:8 Method: Fast for 16 hours, eat within an 8-hour window (e.g., noon to 8 PM).
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally for 5 days, restrict calories to 500–600 for 2 days.
- OMAD (One Meal A Day): Consume one large meal a day, fast for the remaining 23 hours.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Rotate between normal eating days and fasting days.
How Intermittent Fasting Works
The Science of Metabolic Switching
After about 12 hours of fasting, your body switches from using glucose to burning fat for energy. This process is called metabolic switching, and it’s a key reason why IF is effective for weight loss and overall health.
Autophagy and Hormonal Impact
Fasting triggers autophagy, a process where the body cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new ones. Additionally, IF balances insulin, human growth hormone, and other metabolic hormones that influence fat storage and energy use.
1. Supports Healthy Weight Loss
Reduced Caloric Intake
By limiting your eating window, you naturally consume fewer calories—without strict calorie counting. This helps create a calorie deficit essential for weight loss.
Enhanced Fat Burning
Fasting increases norepinephrine levels, which boosts metabolism and promotes fat breakdown. Combined with lowered insulin levels, it helps target stubborn fat, especially around the belly.
2. Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Intermittent fasting lowers blood sugar levels and helps the body become more insulin sensitive. That means glucose is processed more efficiently, reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Numerous studies suggest intermittent fasting can significantly lower the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving glycemic control and reducing fasting insulin levels.
3. Boosts Metabolism Naturally
Human Growth Hormone Increase
During fasting, HGH levels can rise by as much as 5-fold, aiding muscle gain, fat loss, and overall metabolic health.
Cellular Repair and Efficiency
Fasting stimulates cell repair processes, including autophagy, which improves the function and longevity of mitochondria—your cellular powerhouses.
4. Enhances Brain Function and Mental Clarity
BDNF Production
Fasting boosts the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports neuron growth and function, enhancing cognitive performance.
Neuroprotective Benefits
Research indicates intermittent fasting may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
5. Reduces Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Anti-inflammatory Markers
Intermittent fasting reduces inflammatory markers such as CRP and IL-6, contributing to a lowered risk of chronic diseases.
Cellular Rejuvenation
The fasting state triggers antioxidant defenses, helping neutralize harmful free radicals and protect against premature aging.
6. Promotes Heart Health
Cholesterol Regulation
Studies show that intermittent fasting can improve cholesterol levels by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
Lower Blood Pressure
Fasting has been associated with decreased blood pressure levels, which reduces the strain on your heart and blood vessels.
7. May Help Prevent Cancer
Cell Regeneration and Detox
Fasting initiates cellular apoptosis—a process that removes damaged cells, potentially reducing cancer risks.
Fasting in Chemotherapy Research
Emerging studies suggest that fasting might enhance chemotherapy effectiveness and reduce its side effects by protecting healthy cells.
8. Supports Longevity and Anti-Aging
Caloric Restriction Benefits
Fasting mimics caloric restriction, one of the most well-researched methods to extend lifespan across various species.
Mitochondrial Health
Fasting enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, which increases energy efficiency and reduces signs of aging at a cellular level.
9. Improves Gut Health and Digestion
Gut Microbiome Reset
Intermittent fasting allows the gut to rest, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and improving gut lining integrity.
Reduced Bloating and IBS Symptoms
Many people report a reduction in bloating and symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) after adopting a fasting routine.
10. Enhances Hormonal Balance
Effects on Cortisol, Leptin, and Ghrelin
Fasting balances key hunger and stress hormones. It reduces cortisol, regulates ghrelin (hunger hormone), and improves leptin sensitivity, helping with appetite control.
Female Hormonal Considerations
Women may respond differently to IF. Shorter fasting windows (like 14:10) and tailored plans are recommended for hormonal harmony.
Tips to Start Intermittent Fasting Safely
Choosing the Right Fasting Method
When starting intermittent fasting, it’s crucial to choose a method that aligns with your lifestyle. Here are some beginner-friendly tips:
- Start with the 12:12 method: Fast for 12 hours, eat for 12 hours. This is an easy entry point before moving to more advanced methods like 16:8.
- Gradually increase fasting window: Avoid jumping into long fasts. Increase your fasting window by 1–2 hours every few days.
- Stay hydrated: Water, herbal teas, and black coffee are fasting-friendly and help curb hunger.
- Break the fast wisely: Avoid high-sugar or processed foods. Opt for a meal rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Skipping meals without planning: Always plan your meals to ensure you’re getting adequate nutrients during your eating window.
- Overeating during the feeding period: Fasting isn’t a license to binge. Maintain portion control and eat mindfully.
- Not listening to your body: If you feel lightheaded or weak, it’s okay to adjust your fasting plan or stop.
Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting?
While intermittent fasting offers numerous benefits, it’s not suitable for everyone.
Medical Conditions and Special Cases
- Individuals with a history of eating disorders should avoid IF as it might trigger unhealthy habits.
- People with diabetes (especially those on insulin) must consult a doctor before starting IF to avoid dangerous blood sugar drops.
- Those with chronic stress or adrenal fatigue might find fasting adds more strain to their system.
Precautions for Pregnant Women and Diabetics
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should focus on nutrient-rich, regular meals rather than fasting.
- Diabetics should work closely with healthcare providers to monitor insulin levels and medication timing.
Success Stories and Research Backing
Scientific Studies
Numerous peer-reviewed studies support the benefits of intermittent fasting:
- A 2019 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine highlighted fasting’s role in cellular repair, metabolism, and disease prevention.
- A 2018 review in Cell Metabolism concluded that IF could help reduce obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation.
Real-Life Testimonials
Many individuals report personal success stories such as:
- Weight loss transformations
- Mental clarity improvements
- Resolution of chronic digestive issues
These real-world examples reinforce the power of this simple, flexible health strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is intermittent fasting safe long term?
Yes, for most healthy individuals, intermittent fasting is safe long term. However, it’s important to monitor your body’s response and get regular checkups.
2. Can I drink coffee during fasting?
Yes, black coffee (without cream or sugar) is allowed during fasting periods and may even support fat-burning due to its caffeine content.
3. What breaks a fast?
Any food or drink with significant calories breaks a fast. This includes juice, milk, and anything with sugar. Stick to water, black coffee, or tea.
4. Is it okay to work out while fasting?
Yes. Many people successfully train fasted, especially for light to moderate workouts. For intense training, you might need to adjust your eating window or meal timing.
5. Does intermittent fasting work for women?
It can, but women should approach it differently. Some research suggests shorter fasting windows (14:10) may be better to maintain hormonal balance.
6. How long does it take to see results?
Results vary, but many people begin noticing weight loss and improved energy within 2–4 weeks. Deeper metabolic benefits may take a few months.
Conclusion: Is Intermittent Fasting Right for You?
Intermittent fasting is more than a trend—it’s a scientifically-backed lifestyle that offers real benefits. From weight loss and improved metabolic health to enhanced brain function and longevity, IF is a powerful tool for wellness when practiced correctly.
But it’s not one-size-fits-all. Start slowly, listen to your body, and consider consulting a healthcare provider—especially if you have underlying health concerns.
Whether you’re aiming to shed pounds, improve mental clarity, or simply adopt a more mindful eating routine, intermittent fasting may be the life-changing shift you’ve been searching for.